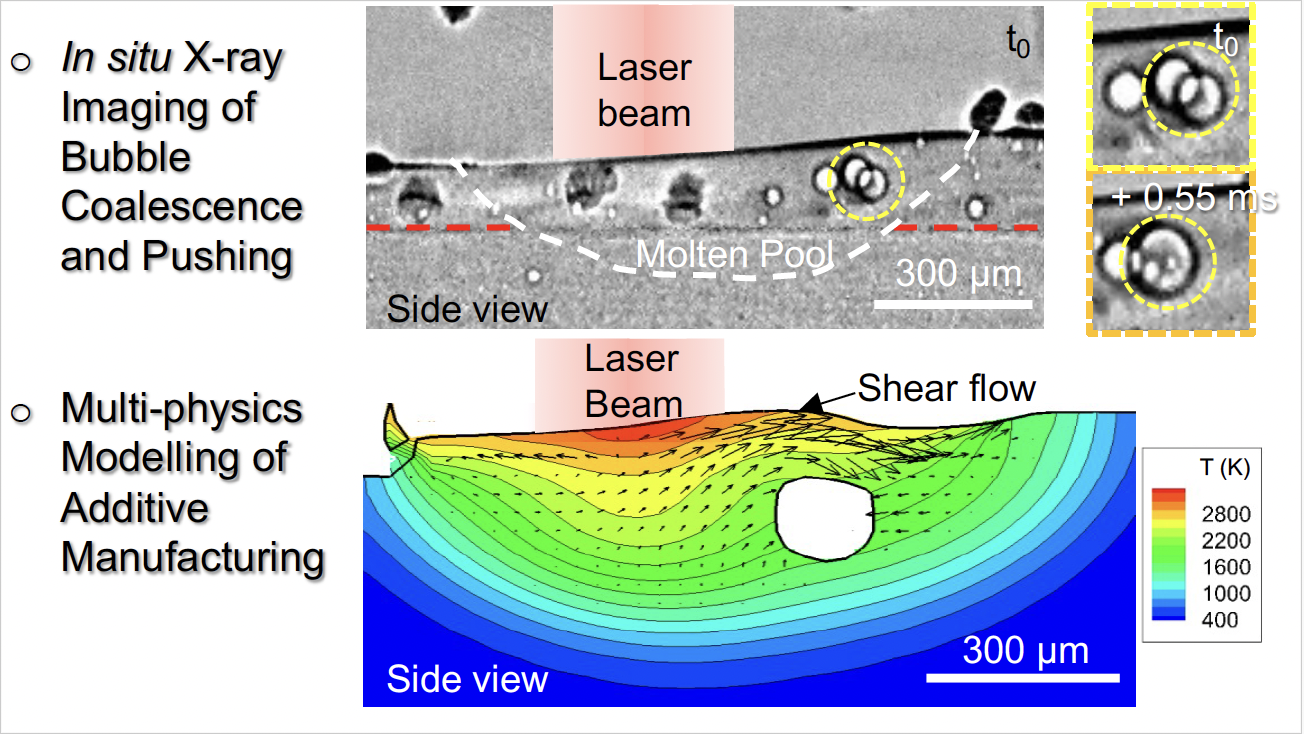
All Publications /
Publications:
Thermal near infared monitoring system for electron beam melting with emissivity tracking
10 / 01 / 19
PAPER: Thermal near infared monitoring system for electron beam melting with emissivity tracking
PUBLICATION: Additive Manufacturing (2018)
AUTHORS: Boone, N., Zhu, C., Smith, C., Todd, I., Willmott, J.R.
In additive manufacturing (AM) parts are created from Computer Aided Design (CAD) models.
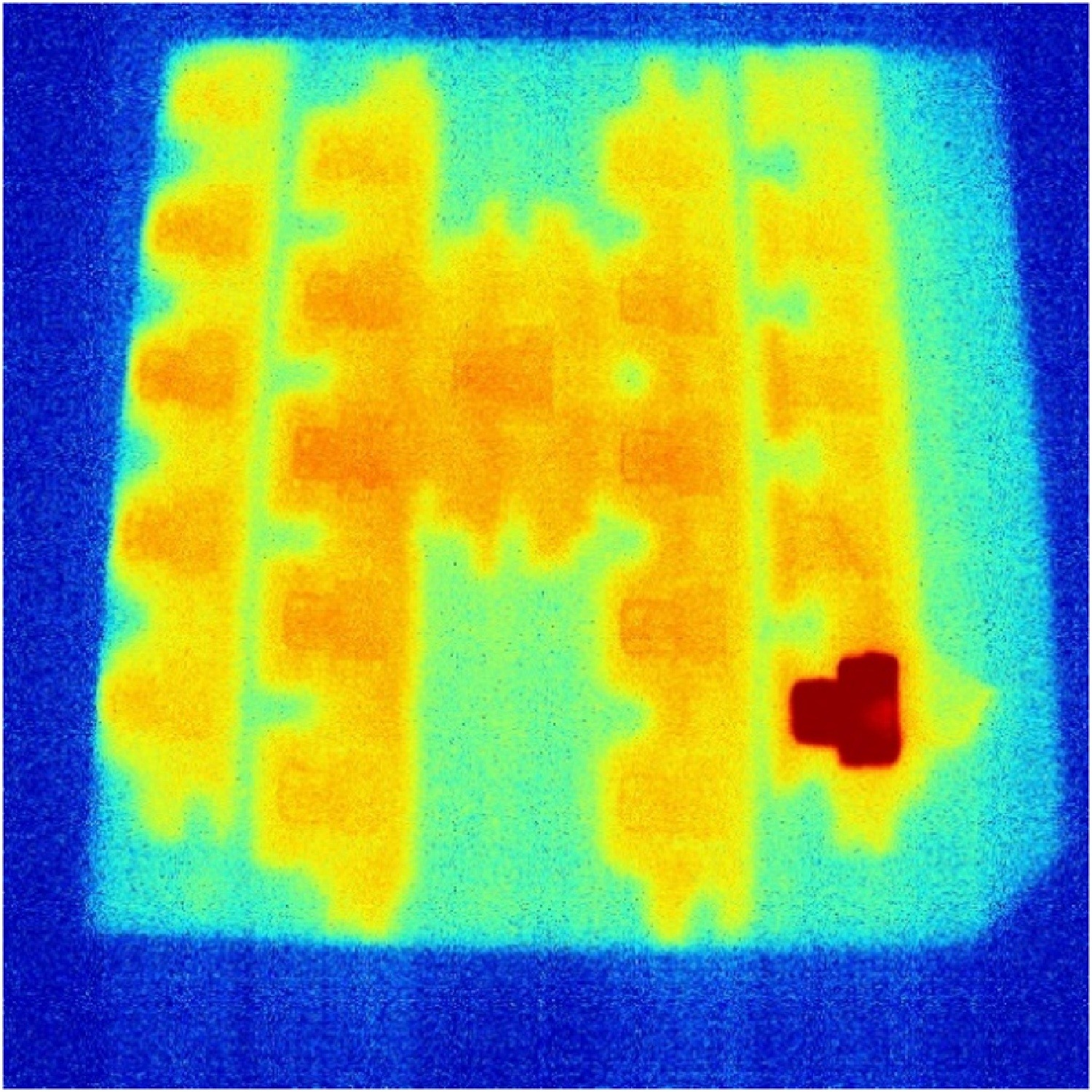
Parts can currently have dimensional variations, rough surface finishes and internal defects not present in the Computer Aided Design (CAD) models used to create them.
Improved in-process monitoring systems could be the solution to this problem which can act as a barrier to uptake.
Thermal imaging is ideal for AM in-process monitoring because AM processes typically rely upon heat to fuse particles of deposited materials.
This paper presents the design of a high speed, high resolution, silicon based thermal imaging instrument.
It was used to thermally image the temperature distributions of an electron beam melting AM system.
The system is showing details within thermal fields not seen before.
The paper states: “With this new instrument, in-situ thermal imaging of the entire build area has been made possible at high speed, allowing defect detection and melt pool tracking.” (Boone et al. 2018, p601)
Melt pool tracking was used to implement an emissivity correction algorithm - an important step towards accurate contactless temperature measurement in the Electron Beam Melting (EBM) environment.
The report discusses the advantages of this technology compared to other thermal imaging methods.
The system brings higher speed and spatial resolution over existing solutions, together with an accurate temperature calibration.
It is ideal for in process monitoring of AM systems like EBM thanks to advantages including high resolution and a high frame rate.
The authors anticipate their system will allow accurate online detection of defects based on high speed image analysis in the future.
Click here to view the paper.
More:
Publications
-
-
X1 Case Study B (UCL)
Impact of powder oxidation during additive manufacturing
Investigators: Prof Peter Lee
Researchers: Prof Chu...