All Publications /
Publications:
Synchrotron X-ray imaging of directed energy deposition additive manufacturing of titanium alloy Ti-6242
06 / 07 / 21
Paper: Synchrotron X-ray imaging of directed energy deposition additive manufacturing of titanium alloy Ti-6242
Authors: Chen, Y., Clark, S.J., Sinclair, L., Leung, C.L.A., Marussi, S., Connolley, T., Atwood, R.C., Baxter, G.J., Jones, M.A., Todd, I., Lee, P.D.
Publication: Additive Manufacturing
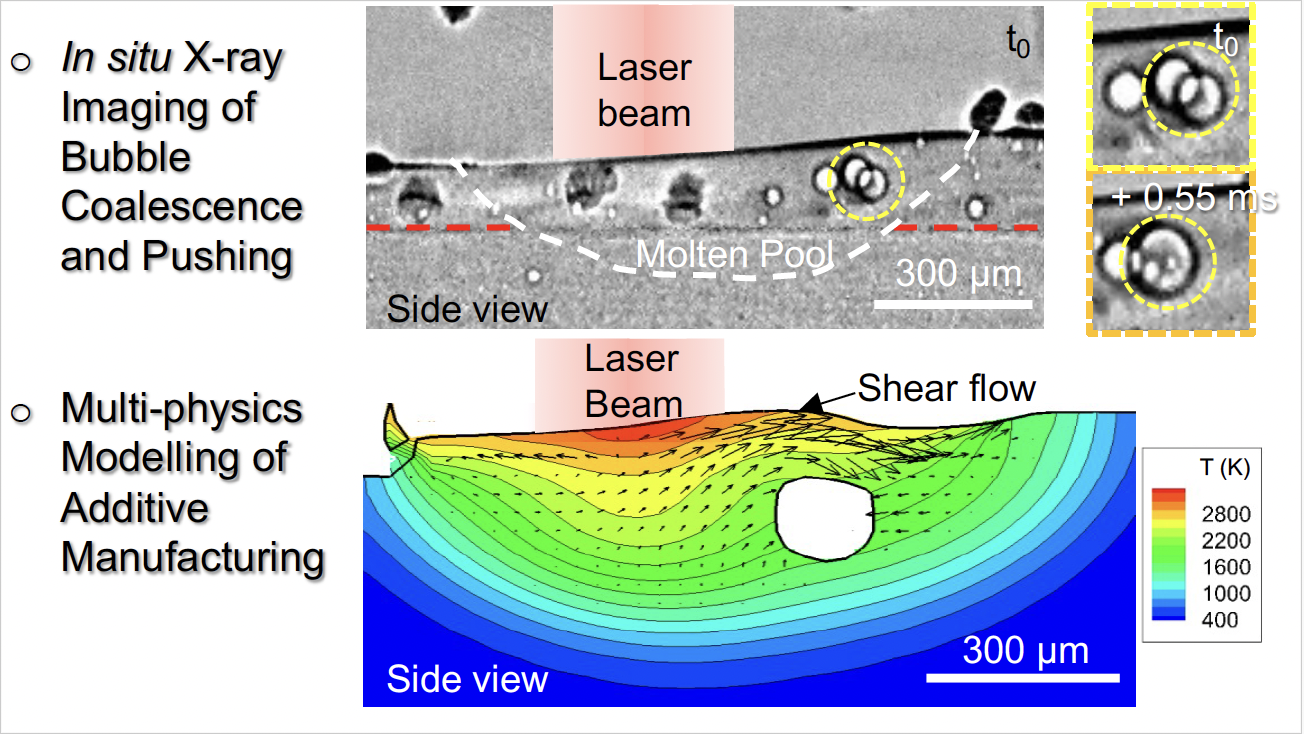
MAPP researchers have published a paper that enhances the fundamental understanding of the Directed Energy Deposition additive manufacturing (DED-AM) process.
In-situ and operando synchrotron X-ray imaging was used to reveal key information about DED-AM of Ti-6242 that can be used as a guide for optimising industrial additive manufacturing (AM) processes.
To replicate a commercial laser DED-AM system for use on synchrotron beamlines a custom-built blown powder additive manufacturing process replicator (BAMPR) was used.
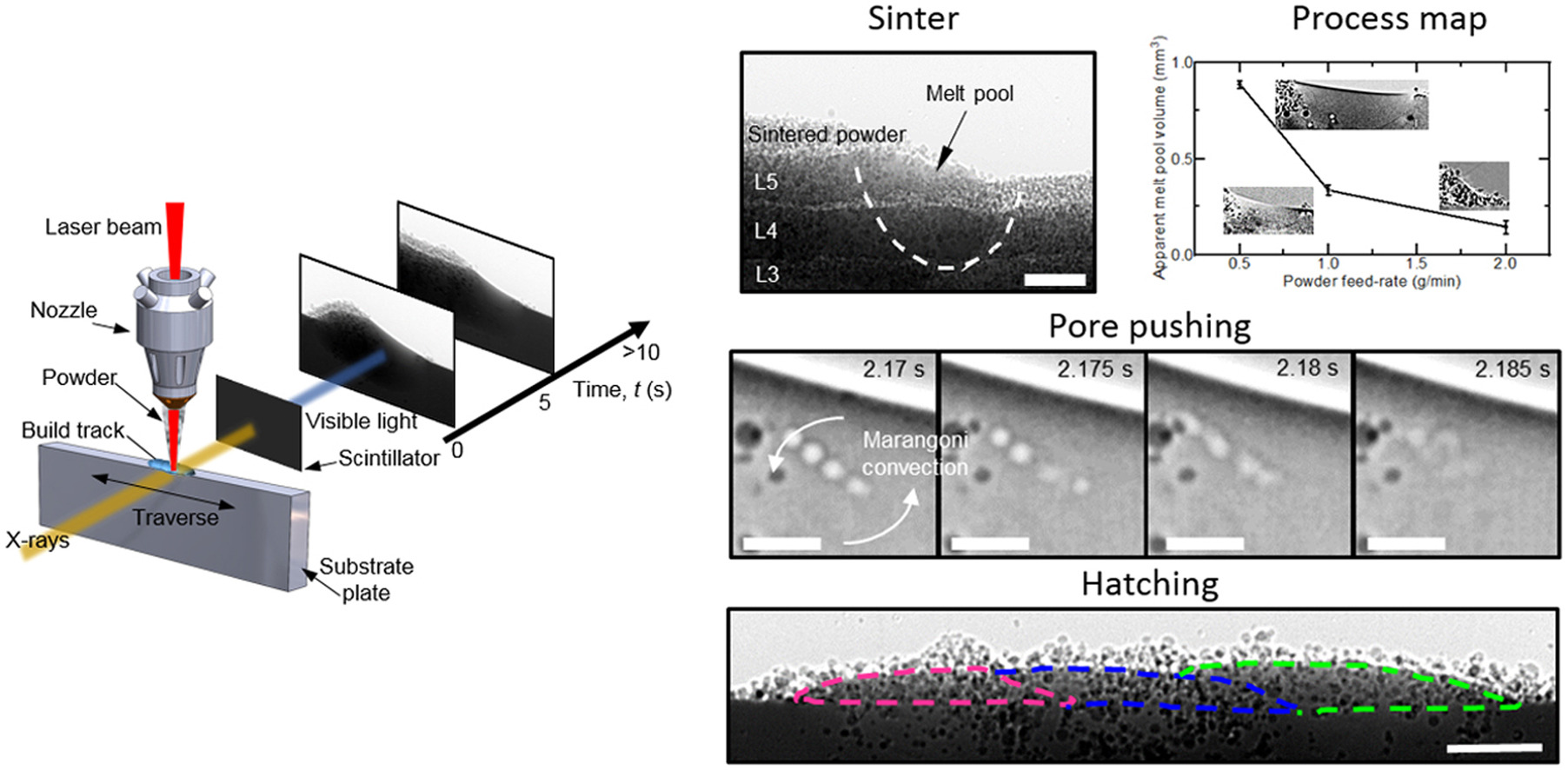
Using different build strategies, the authors observed single track deposit evolution, melt pool morphology and multilayer build phenomena.
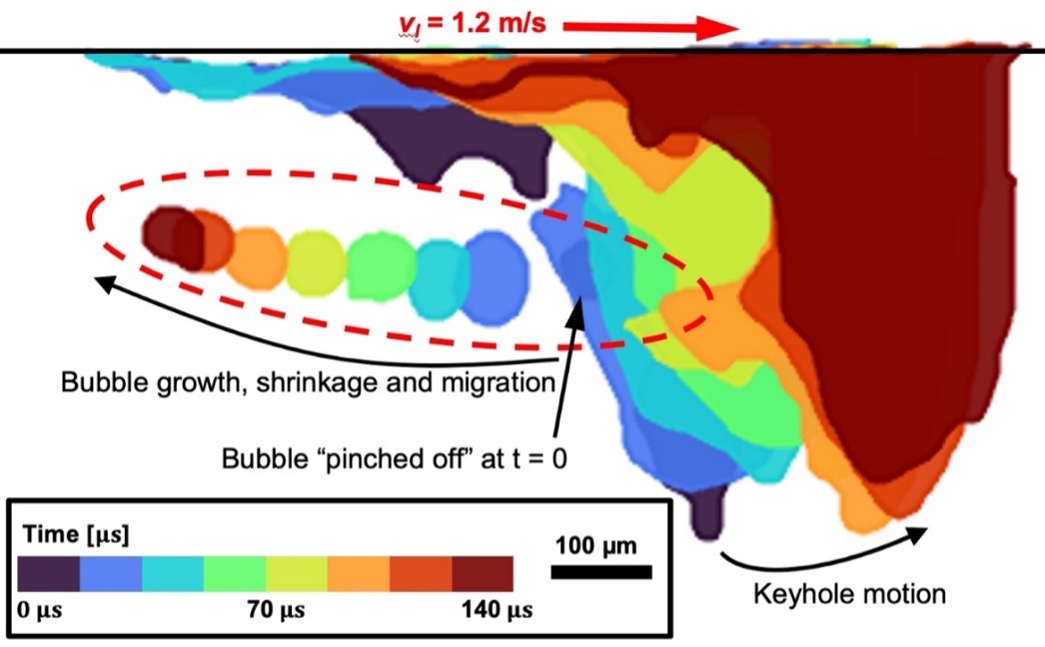
They also gained an increased understanding of gas pore formation and dynamics.
Analysis of the process conditions revealed that laser power is dominant for build efficiency while higher traverse speed can effectively reduce lack of fusion regions.
Click here to view the paper.
Image reprinted from Additive Manufacturing, 41, Chen,Y., et. al., Synchrotron X-ray imaging of directed energy deposition additive manufacturing of titanium alloy Ti-6242, 101969., Copyright (2021), with permission from Elsevier.
More:
Publications
-
-
X1 Case Study B (UCL)
Impact of powder oxidation during additive manufacturing
Investigators: Prof Peter Lee
Researchers: Prof Chu...