All Publications /
Publications:
A multi-laser approach with the potential to overcome traditional laser powder bed fusion processing challenges
07 / 06 / 22
Paper: Diode area melting of Ti6Al4V using 808 nm laser sources and variable multi-beam profiles.
Authors: Alsaddah, M., Khan, A., Groom, K., Mumtaz, K.
Publication: Materials & Design
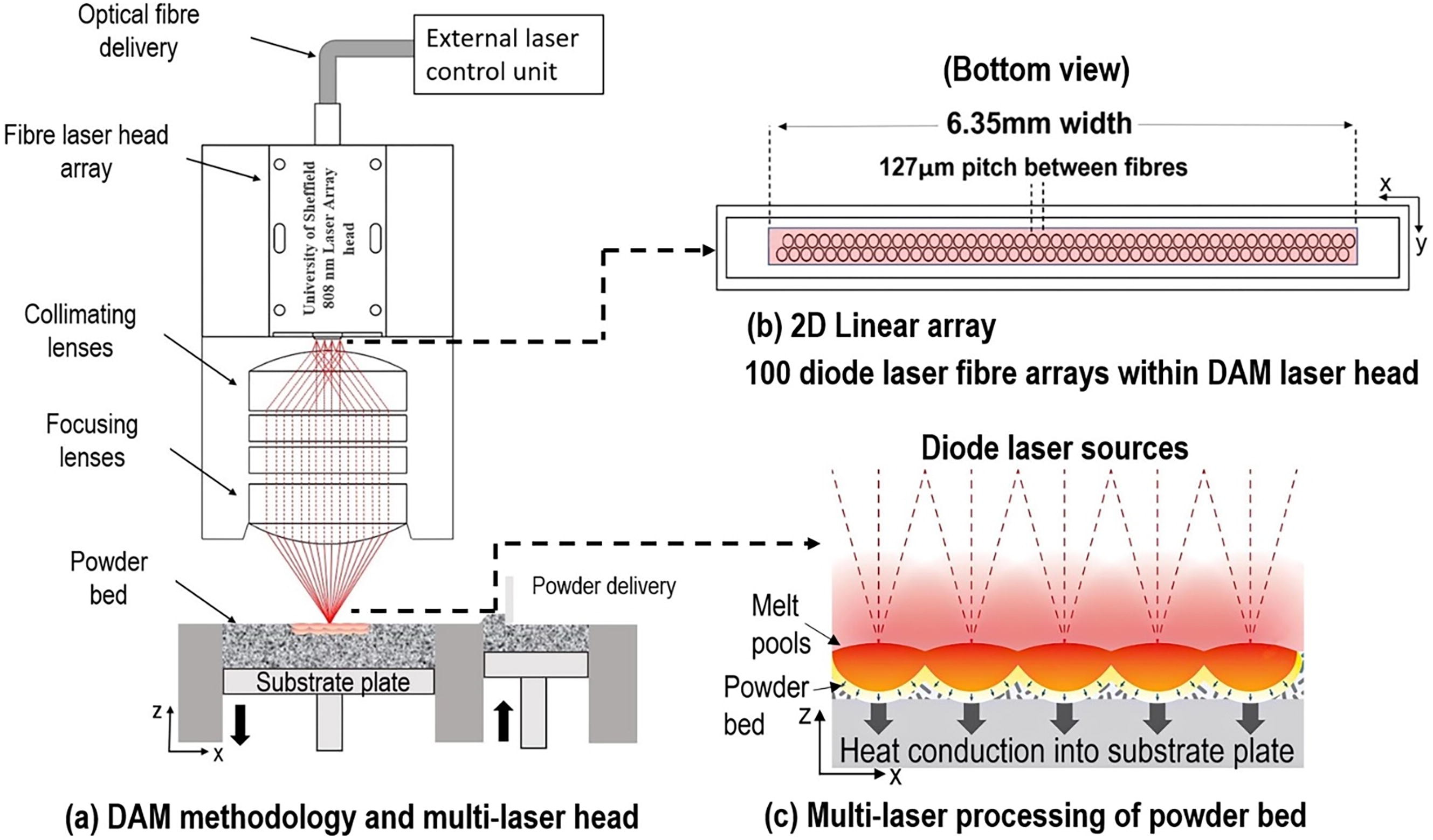
This paper presents a multi-laser approach with the potential to overcome traditional laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) processing challenges like scalability, processing efficiency and thermal control.
The Diode Area Melting (DAM) process integrates multiple individually addressable low power fibre coupled diode lasers into a laser head, these traverse across a powder bed to melt powdered feedstock.
The highly scalable and compact diode lasers operate at a shorter wavelength and lower powers compared to traditional LPBF fibre lasers, enabling a more efficient energy absorption.
In this study, a bespoke multi-laser head was used to process Ti6Al4V powder using ten 5 W 808 nm diode lasers simultaneously. Multi-layer parts were produced with a maximum density of 98% with variable beam profiles shown to greatly influence melt pool formation, microstructure and mechanical performance.
Click here to view the paper.
More:
Publications
-
-
X1 Case Study B (UCL)
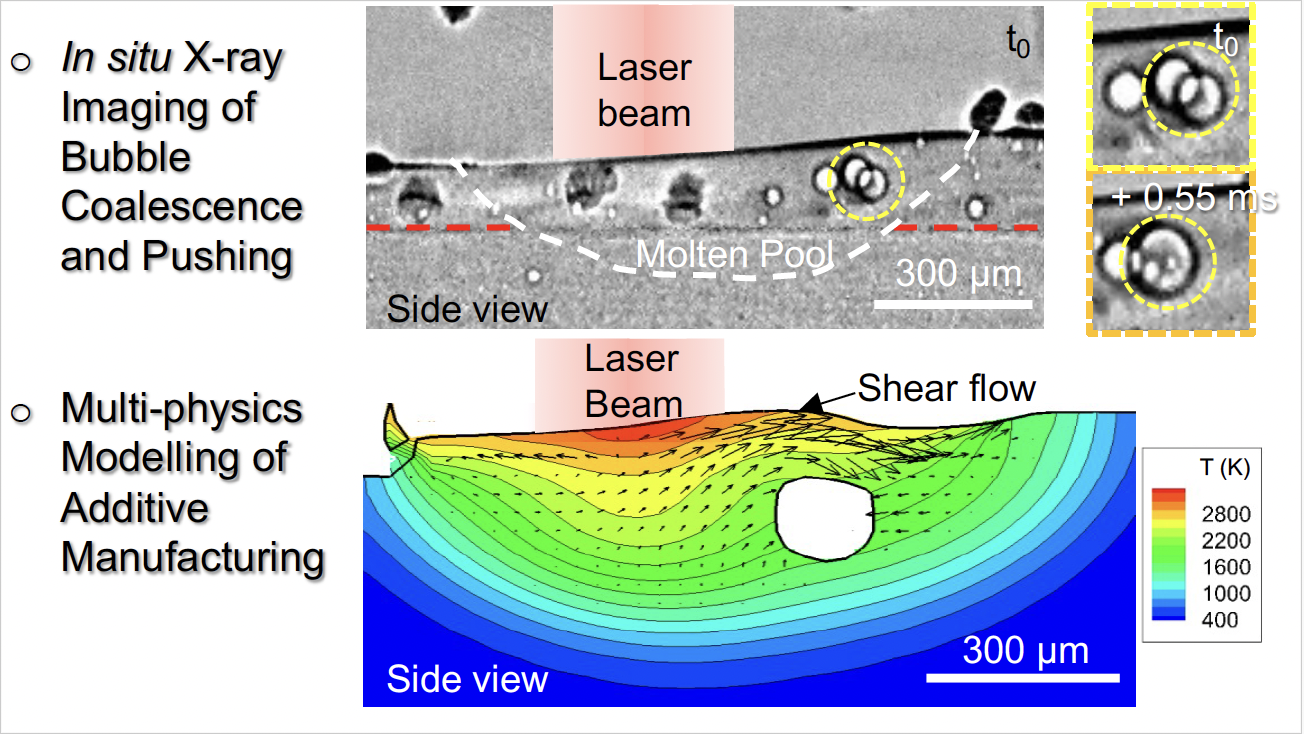
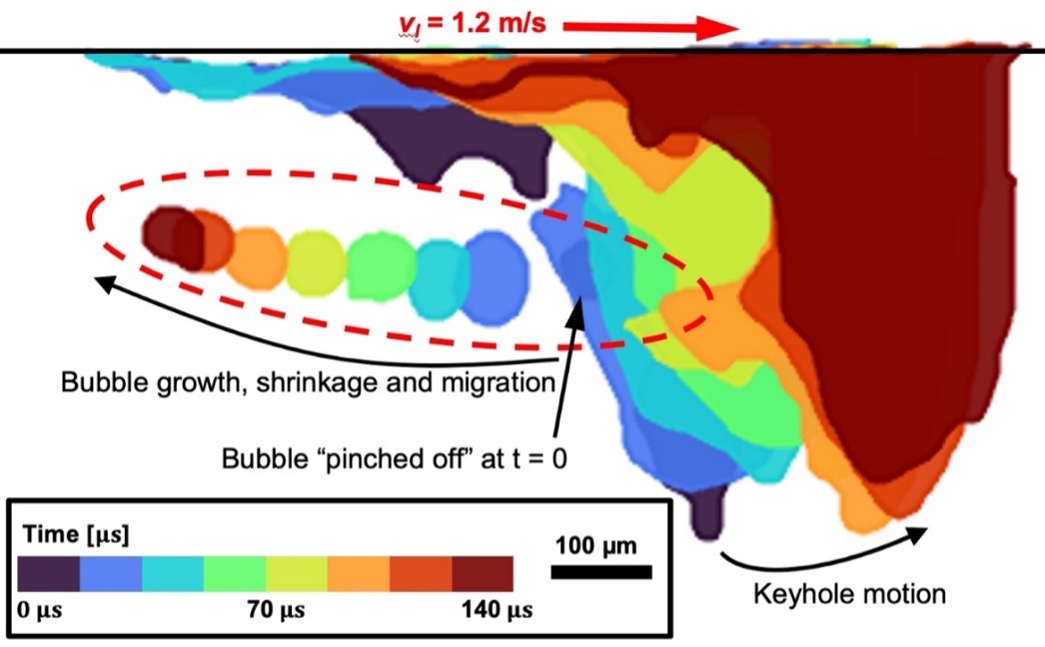
Impact of powder oxidation during additive manufacturing
Investigators: Prof Peter Lee
Researchers: Prof Chu...